花の寿命を支配している遺伝子群の同定

メンバー: 山田哲也、金勝一樹
分野: 生産環境農学、境界農学、生物科学
所属: 農学研究院
キーワード: 細胞老化、プログラム細胞死、花弁老化、花持ち性、アサガオ、花弁展開、次世代シーケンサー、トランスクリプトーム
ウェブサイト:
研究概要
花の寿命に関わる花弁老化などの形質について知見が集積されているアサガオを実験モデルとして用い、花持ち性の品種改良に利用可能な有用遺伝子の同定を目的として、以下の研究を実施しています。
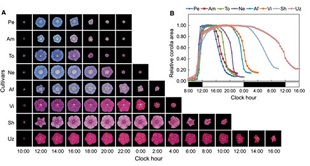
1)画像解析法を用いた花冠面積の経時的調査による花弁老化の開始時刻に顕著な差異のあるアサガオ系統の探索
2)RNA-seq法やSSH法を用いた花弁老化に差異のあるアサガオ系統間の花弁における比較発現解析による老化関連遺伝子の選抜
3)RNAi法やVIGS法を用いた花弁老化関連遺伝子の発現抑制による遺伝子機能の解析および有用遺伝子の同定
主要論文・参考事項
1) Yamada T, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG (2007) Gene expression in opening and senescing petals of morning glory (Ipomoea nil) flowers. Plant Cell Rep 26: 823–835.
2) Shibuya K, Yamada T, Suzuki T, Shimizu K, Ichimura K (2009) InPSR26, a putative membrane protein, regulates programmed cell death during petal senescence in Ipomoea nil. Plant Physiol 149: 816-824.
3) Yamada T, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG (2009) Homologues of genes associated with programmed cell death in animal cells are differentially expressed during senescence of Ipomoea nil petals. Plant Cell Physiol 50: 610-625.
4) 七夕高也,山田哲也,清水悠介,篠崎良仁,金勝一樹,高野誠(2010)植物器官のデジタル画像面積を効率的に計測できる領域抽出ソフトウエアの開発.園学研 9: 501-506.
5) Shinozaki Y, Tanabata T, Ogiwara I, Yamada T, Kanekatsu M (2011) Application of digital image analysis system for fine evaluation of varietal differences and the role of ethylene in visible petal senescence of morning glory. J Plant Growth Regul 30: 229-234.
6) Shinozaki Y, Tanaka T, Ogiwara I, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG, Yamada T* (2014) Expression of an AtNAP gene homolog in senescing morning glory (Ipomoea nil) petals of two cultivars with a different flower life span. J Plant Physiol 171: 633-638.
7) Ono H, Ishii K, Kozaki T, Shimizu K, Shibuya K, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, Yamada T (2014) InPSR42, a putative 14-3-3 protein, regulates petal opening and senescence in Japanese morning glory. The 29th International Horticultural Congress.
お問い合わせ先
東京農工大学・先端産学連携研究推進センター
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp([at]を@に変換してください)
Identification of genes involved in flower longevity

Research members: Tetsuya Yamada PhD., Motoki Kanekatsu PhD.
Research fields: Plant production and environmental agriculture, Boundary agriculture, Biological Science
Departments: Institute of Agriculture
Keywords: cellular senescence, programmed cell death, petal senescence, flower longevity, morning glory, petal opening, next-generation sequencer, transcriptome analysis
Web site:
Summary

Identification of useful genes available for breeding of flower longevity has been performed by using morning glory which has been studied about flower longevity-related traits such as petal senescence.
1) Screening of morning glory strains showing significant difference in onset times of petal senescence by time-course analysis of corolla area using image analysis
2) Selection of genes by comparative expression analysis in the petals between the morning glory strains showing differences in petal senescence by using RNA-Seq or SSH method
3) Analysis of gene function and identification of useful gene by suppression of genes related to petal senescence using RNAi or VIGS method
Reference articles and patents
1) Yamada T, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG (2007) Gene expression in opening and senescing petals of morning glory (Ipomoea nil) flowers. Plant Cell Rep 26: 823–835.
2) Shibuya K, Yamada T, Suzuki T, Shimizu K, Ichimura K (2009) InPSR26, a putative membrane protein, regulates programmed cell death during petal senescence in Ipomoea nil. Plant Physiol 149: 816-824.
3) Yamada T, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG (2009) Homologues of genes associated with programmed cell death in animal cells are differentially expressed during senescence of Ipomoea nil petals. Plant Cell Physiol 50: 610-625.
4) 七夕高也,山田哲也,清水悠介,篠崎良仁,金勝一樹,高野誠(2010)植物器官のデジタル画像面積を効率的に計測できる領域抽出ソフトウエアの開発.園学研 9: 501-506.
5) Shinozaki Y, Tanabata T, Ogiwara I, Yamada T, Kanekatsu M (2011) Application of digital image analysis system for fine evaluation of varietal differences and the role of ethylene in visible petal senescence of morning glory. J Plant Growth Regul 30: 229-234.
6) Shinozaki Y, Tanaka T, Ogiwara I, Kanekatsu M, van Doorn WG, Yamada T* (2014) Expression of an AtNAP gene homolog in senescing morning glory (Ipomoea nil) petals of two cultivars with a different flower life span. J Plant Physiol 171: 633-638.
7) Ono H, Ishii K, Kozaki T, Shimizu K, Shibuya K, Ichimura K, Kanekatsu M, Yamada T (2014) InPSR42, a putative 14-3-3 protein, regulates petal opening and senescence in Japanese morning glory. The 29th International Horticultural Congress.
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)