最適性を保証する直線・平面の認識
メンバー: 清水郁子
分野: 人間情報学、情報学フロンティア
所属: 工学研究院先端情報科学部門
キーワード: 知能情報学、センサ情報処理、コンピュータビジョン、画像認識
ウェブサイト:
研究概要

近年、対象までの距離を直接計測することが可能な距離センサ(レーザレーダや赤外線センサなど)がロボットや車などに搭載され、周辺環境を認識するために用いられている。このようなセンサにより、空間の断面や、断面を複数方向で得て3次元的な形状が得られたりする。建物の計測などの応用を考えると、このようなデータから直線や平面を認識することは非常に重要である。
従来手法では、RANDom Sample Consensus(RANSAC)法が用いられることが一般的であった。RANSACでは、推定したい平面上にある計測点が一定の割合で計測データ中に含まれていることを仮定し、計測点集合からランダムに3点サンプリングすることを繰り返し、3点で張られる平面からの距離が閾値以内の計測点数をカウントし、しかしながら、本研究で対象としているデータでは、空間的な計測点の分布が不均一であるため、望みの結果が得られない場合が多い。また、与えた閾値により得られる結果は大きく異なる。
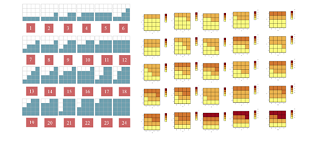
我々は、ユーザが何らかのパラメタを指定することなく、空間的な分布が不均一なデータから頑健に直線・平面を認識する手法を提案している。我々の手法は、注目点とその近傍のボクセルのみから、注目点が平面上にあるかどうかを判定するための離散平面パターンに基づく。本研究では、解像度の間での不変性が保証される直線・平面のモデルを用いる。解像度のの変更を容易にするために、4X4の大きさのピクセル、4X4X4の大きさのボクセルを近傍領域とする。これにより、解像度の変更を行いより高い解像度での平面検出を行う場合、注目点を含む1/4の大きさのボクセルに着目すればよくなる。
直線パターンの生成は、4X4の近傍ピクセルのうち、注目点を除く4X4-1個のピクセルについて、直線に含まれる(あるいは直線上にある)場合と直線に含まれない場合の全ての組合せを生成し、その点の配置の組合せが直線の式を満たすかどうか判定することにより行った。平面パターンを生成する場合も同様に、4X4X4の近傍ボクセルのうち、注目点を除く4X4X4-1個のボクセルについて、平面に含まれる(あるいは平面上にある)場合と平面に含まれない場合の全ての組合せを生成し、その点の配置の組合せが平面の式を満たすかどうか判定することにより行うことができる。しかしながら、4X4X4-1個のボクセルそれぞれが平面の内側か外側かの全ての組合せを生成すると組合せ数が膨大になり、計算できない。そのため、本研究では、平面の2次元の断面は必ず直線になることを利用し、直線パターンの組合せに寄り、平面パターンを生成した。さらに、解像度間でのパターンの関係も明らかにした。
これらの直線パターン・平面パターンと局所的な領域をマッチングすることにより、注目している点が直線上(平面上)にあるかどうか、そして、直線上(平面上)にある場合、直線(平面)のパラメタはどのような範囲にあるかの判定ができるようになった。
主要論文・参考事項
・山田眞伍,清水郁子,"剛体変換の整合性を保証する大域収束する距離画像の位置合わせ",電子情報通信学会和文誌D,Vol.J95-D,No.11,pp.1944-1952, 2012.11
・宮武孝尚,中力雅人,清水郁子,"最適性を保証する多重解像度表現を用いた離散直線当てはめ",情報処理学会論文誌数理モデル化と応用,Vol.5, No.3, pp.107-119, 2012.9
・Rita Zrour, Yukiko Kenmochi, Hugues Talbot, Lilian Buzer, Yskandar Hamam, Ikuko Shimizu, Akihiro Sugimoto, "Optimal consensus set for digital line and plane fitting", International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, Vol 21, Vol. 1, pp.45-57, 2011.2
・Takahisa Miyatake, Ikuko Shimizu, "Generating discrete line patterns",International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT 2015), 2015.1
・Yuko Shikanai, Ikuko Shimizu, "Plane detection in the large scale 3D point cloud based on local discrete plane patterns",International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT 2015), 2015.1
お問い合わせ先
東京農工大学・先端産学連携研究推進センター
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp([at]を@に変換してください)
Optimal Recognition for Line and Plane Recognition

Research members: Ikuko Shimizu PhD.
Research fields: Human informatics, Frontiers of informatics
Departments: Division of Advanced Information Technology&Computer Science, Institute of Engineering
Keywords: Intelligece Science and Technology, Sensor Information Analysis, Computer vision, Image Recognition
Web site:
Summary

Recently, large scale 3D point cloud data becomes popular as development of 3D sensing technology. Applications are renovation of historic buildings, management of social infrastructure facilities, and so on. Recognition of Plane in 3D point cloud is important because many buildings to be measured are consists of planes. Local method for plane recognition has an advantage to deal with large scale data. A set of measured 3D point cloud consists of several millions of points.
The number of a set of 3D points is very large scanned by general 3D laser scanner for building measurement. Density of the 3D point is not uniform depending on the distance to the scanner and the angle between laser beam and the scanned surface.
One of the conventional methods is based on RANSAC (RANdom SAmple Consensus). This method randomly selects three points for detecting plane and calculate the distance from the rest of points to the to the plane estimated by the selected three points. When the number of points whose distances are less than the threshold becomes enough large, the algorithm stops. It often fails for the data which has a quite dense part when it samples all three points from the dense part and the number of points whose distance to the plane estimated by these points are less than the threshold would be enough large.
Our method for digital line recognition in 2D and digital plane recognition in 3D is developped to deal with the large scale point cloud with non-uniform density.It decides a point is on a plane or not and the feasible region of plane parameters by local operation. and can be applied hierarchically from coarse to fine.
We focus on the interest point and its neighboring pixels in 2D and voxels in 3D.
To guarantee detecting the same lines and patterns, we investigate 4X4 neighbors in 2D and 4X4X4 neighbors in 3D. “Pattern” is the combinations of the labels which describe each pixel or voxel is inside of the line or plane or outside of the line or plane. If the interest point is on a line in 2D and all pixels in the 4X4 neighbors can be explained by the same line, the patterns of neighboring pixels are highly restricted though the 4X4 neighbors can be 2^{4x4} possibilities.
If the interest point is on a plane in 3D and all voxels in the 4X4x4 neighbors can be explained by the same plane, the patterns of neighboring voxels are highly restricted though the 4X4X4 neighbors can be 2^{4x4x4} possibilities.
Reference articles and patents
・山田眞伍,清水郁子,"剛体変換の整合性を保証する大域収束する距離画像の位置合わせ",電子情報通信学会和文誌D,Vol.J95-D,No.11,pp.1944-1952, 2012.11
・宮武孝尚,中力雅人,清水郁子,"最適性を保証する多重解像度表現を用いた離散直線当てはめ",情報処理学会論文誌数理モデル化と応用,Vol.5, No.3, pp.107-119, 2012.9
・Rita Zrour, Yukiko Kenmochi, Hugues Talbot, Lilian Buzer, Yskandar Hamam, Ikuko Shimizu, Akihiro Sugimoto, "Optimal consensus set for digital line and plane fitting", International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, Vol 21, Vol. 1, pp.45-57, 2011.2
・Takahisa Miyatake, Ikuko Shimizu, "Generating discrete line patterns",International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT 2015), 2015.1
・Yuko Shikanai, Ikuko Shimizu, "Plane detection in the large scale 3D point cloud based on local discrete plane patterns",International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT 2015), 2015.1
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)

