各種環境条件下における黄色ブドウ球菌のエンテロトキシン生成と増殖
メンバー: 藤川浩
分野: 動物生命科学、社会医学
所属: 農学研究院農学部共同獣医学科
キーワード: 黄色ブドウ球菌、エンテロトキシン、増殖、生乳、乳製品、環境ストレス、増殖モデル、温度積算計
研究概要

2000年にブドウ球菌産生エンテロトキシン(A型)に汚染された低脂肪乳製品の摂取による大規模な食中毒事件が大阪で起きた。製造中の事故が原因と考えられているが、なぜ生乳中で本菌が増殖し、エンテロトキシンを生成できたかは明らかではなかった。
そこで、まず市販牛乳中での本菌の増殖およびエンテロトキシン生成量を各種温度下で測定した。そのデータを数学モデルで解析し、新たな変動する温度下での本菌の増殖と毒素産生量を精確に予測できた。
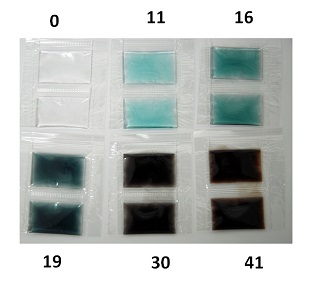
各種の環境由来微生物に汚染された生乳について、黄色ブドウ球菌を接種し、各種温度で保存してその増殖と毒素生成を検討した。その結果、特に汚染菌数の高い生乳では、40-44℃でのみ本毒素生成が認められた。この温度は大阪での事件で生乳が保管されていた温度であったため、この保管温度が毒素生成に大きな影響を及ぼしたと考えられた。一方、生乳中では本菌の増殖に温度による明らかな差はなかった。一方、生乳中では生成された毒素量が時間とともに減る現象もみられた。このように、生乳中では本菌と汚染微生物の間に複雑な競合関係がみられた。
現在、さらにこれらの現象の解明に向けた研究を進めている。この研究によって本菌の毒素生成を抑制したり、毒素を失活させる方法を見出せるであろう。
食品の微生物学的安全性を確保するため、食品中の微生物増殖を予測するモデルの開発、温度積算計の検討も行なってきた。
主要論文・参考事項
H. Fujikawa and S. Morozumi. 2005. Modeling Surface Growth of Escherichia coli on Agar Plates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 71 (12):7920-7926.
H. Fujikawa and S. Morozumi. 2006. Modeling Staphylococcus aureus Growth and Enterotoxin Production in Milk. Food Microbiology. 23:260-267.
H. Fujikawa and R. Akimoto. 2011. A New Blue Pigment Produced by Pantoea agglomerans and Its Production Characteristics at Various Temperatures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 77(1): 172-178.
Sakha M. Zaher and H. Fujikawa. 2011. Effect of Native Microflora on the Growth Kinetics of Salmonella Enteritidis Strain 04-137 in Raw Ground Chicken. Journal of Food Protection. 74 (5): 735-742.
M.Z. Sakha and H. Fujikawa. 2012. Growth Characteristics of Salmonella Enteritidis in Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Liquid Egg Products. Biocontrol Sience. 17 (4): 183-190.
M.Z. Sakha and H. Fujikawa. 2013. Prediction of Salmonella Enteritidis in Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Liquid Egg Products with a Growth Model. Biocontrol Sience. 18 (2): 89-93.
H. Fujikawa, K. Munakata, and M.Z. Sakha. 2014. Development of a competitive model for microbial growth in mixed culture. Biocontrol Sience. 19 (2): 61-71.
H. Fujikawa and M.Z. Sakha. 2014. Prediction of microbial growth in mixed culture with a competitive model. Biocontrol Sience. 19 (2): 89-92.
I.I.Sabike, H. Fujikawa, M.Z.Sakha, and A.M.Edris. 2014. Production of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin A in raw milk at high temperatures. Journal of Food Protection. 77 (9): 1612-1616.
H. Rokugawa and H. Fujikawa. 2015. Evaluation of a new Maillard reaction type time-temperature integrator at various temperatures. Food Control. 57:355-361.
お問い合わせ先
東京農工大学・先端産学連携研究推進センター
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp([at]を@に変換してください)
Enterotoxin production and growth of Staphylococcus aureus under various environmental conditions
Research members: Dr. Hiroshi Fujikawa
Research fields: Animal life science, Society medicine
Departments: Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Veterinary Science, Institute of Agriculture
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, enterotoxin, growth, raw milk, milk product, environmental stresses, growth model, Time-temperature integrator
Summary of research elements

An extensive Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning outbreak, affecting a total of over 14,000 individuals who ingested low-fat milk products from a dairy company, occurred in Osaka in 2000. Exposure of the raw milk to high temperatures due to a period of power supply loss during product production in a plant may have been the underlying contributing factor that permitted S. aureus growth and subsequent staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) production in the milk.
We quantitatively studied staphylococcal growth and SEA production in pasteurized milk products at a variety of temperatures and then successfully predicted the growth and SEA production of the microorganism in the product.
Then the toxin production in raw milk was studied. That is, two raw milk samples naturally containing low and high levels of natural microflora (NM) were selected. It was found that the optimal temperatures for SEA production in the two milk types were as high as 40°C and 44°C, in the range of 36°C and 48°C, and that SEA production was dependent on the initial dose of S. aureus. These high temperatures were close to that of the outbreak in Japan. Thus, it was concluded that temperature was critical for the SEA production in raw milk. It was also observed that NM in the milk samples considerably suppressed SEA production, but not staphylococcal growth. On the other hand, the amount of toxin in most milk samples decreased after peaking during the storage.
We are studying the mechanisms for the suppression of the toxin production and the inactiovation of the toxin now, leading to find the methods for the control of staphylococcal enterotoxin in milk and other food products.
We also have developed mathematical growth models and evaluated Time-temperature indicators to maintain the microbial food safety of food.
Reference articles and patents
H. Fujikawa and S. Morozumi. 2005. Modeling Surface Growth of Escherichia coli on Agar Plates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 71 (12):7920-7926.
H. Fujikawa and S. Morozumi. 2006. Modeling Staphylococcus aureus Growth and Enterotoxin Production in Milk. Food Microbiology. 23:260-267.
H. Fujikawa and R. Akimoto. 2011. A New Blue Pigment Produced by Pantoea agglomerans and Its Production Characteristics at Various Temperatures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 77(1): 172-178.
Sakha M. Zaher and H. Fujikawa. 2011. Effect of Native Microflora on the Growth Kinetics of Salmonella Enteritidis Strain 04-137 in Raw Ground Chicken. Journal of Food Protection. 74 (5): 735-742.
M.Z. Sakha and H. Fujikawa. 2012. Growth Characteristics of Salmonella Enteritidis in Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Liquid Egg Products. Biocontrol Sience. 17 (4): 183-190.
M.Z. Sakha and H. Fujikawa. 2013. Prediction of Salmonella Enteritidis in Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Liquid Egg Products with a Growth Model. Biocontrol Sience. 18 (2): 89-93.
H. Fujikawa, K. Munakata, and M.Z. Sakha. 2014. Development of a competitive model for microbial growth in mixed culture. Biocontrol Sience. 19 (2): 61-71.
H. Fujikawa and M.Z. Sakha. 2014. Prediction of microbial growth in mixed culture with a competitive model. Biocontrol Sience. 19 (2): 89-92.
I.I.Sabike, H. Fujikawa, M.Z.Sakha, and A.M.Edris. 2014. Production of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin A in raw milk at high temperatures. Journal of Food Protection. 77 (9): 1612-1616.
H. Rokugawa and H. Fujikawa. 2015. Evaluation of a new Maillard reaction type time-temperature integrator at various temperatures. Food Control. 57:355-361.
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)