Development of High-Performance Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Energy Devices

Research members: Dr. Yoichi Tominaga
Research fields: Applied chemistry, Materials chemistry
Departments: Institute of Engineering
Keywords: Polymer electrolytes, Lithium batteries, Polymer blends, Composites, Carbon dioxide utilization
Web site:
Summary

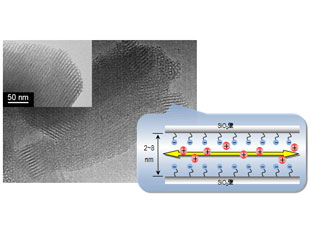
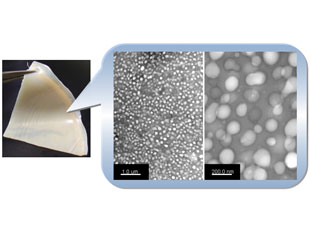
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) such as poly(ethylene oxide)-metal salt complexes have been proposed as solid-state alternatives to liquid electrolytes in electrochemical device applications such as all-polymer lithium batteries. However, SPEs suffer from relatively low ionic conductivity in the solid state compared with most liquid, gel and ceramic electrolytes. For increase in the migration of ions, we have been focusing on compressed carbon dioxide, especially supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) as treatment solvent, utilization of CO2 as monomer (CO2/epoxide copolymers), molecular design for high ionic conductivity, utilization of functional ceramics such as mesoporous silicas and nanofibers, development of polymer blends and composites for SPEs, and development of energy storage/conversion devices such as flexible Li-ion batteries, dye-sensitized solar cells, fuel cells and antistatic materials.
Reference articles and patents
1. Y. Tominaga, T. Maki, Proton-conducting composite membranes based on polybenzimidazole and sulfonated mesoporous organosilicate, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39 (6), 2724-2730 (2014).
2. Y. Tominaga, M. Endo, Polyether-based composite electrolytes filled with mesoporous silica, almina and titania, Electrochimica Acta, 113, 361-365 (2013).
3. S. Kitajima, F. Bertasi, K. Vezz?, E. Negro, Y. Tominaga, V. Di Noto, Dielectric relaxations and conduction mechanisms in polyether/clay composite polymer electrolytes under high carbon dioxide pressure, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 15 (39), 16626-16633 (2013).
4. Y. Tominaga, V. Nanthana, D. Tohyama, Ionic conduction in poly(ethylene carbonate)-based rubbery electrolytes including lithium salts, Polymer Journal, 44 (12) 1155-1158 (2012).
5. Y. Tominaga, T. Shimomura, M. Nakamura, Alternating copolymers of carbon dioxide with glycidyl ethers for novel ion-conductive polymer electrolytes, Polymer, 51 (19), 4295-4298 (2010).
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)