Conservation of biodiversity at Satoyama

Research members: Dr. Munemitsu AKASAKA, Dr. Shinsuke KOIKE, Dr. Toshiyuki TSUCHIYA , Dr. Hiroto TODA, Dr. Yoshinobu HOSHINO, Dr. Tomohiro YOSHIDA
Research fields: Forest and forest products science, Environmental conservation, Sociology
Departments: Environment Conservation, Institute of Agriculture
Keywords: Satoyama, Biodiversity, sika deer browsing, Circulation of Nutrients in Forest Ecosystem, preservation activities
Web site:
Summary

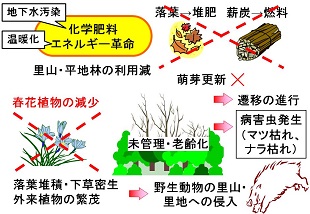
Secondary forest and a mixed forest in the satoyama area is a system that has maintained a high state of biological diversity by being subjected to human influence.
For example, the habitat area of creature in the oak forest have diversified by the repetition of logging and sprout regeneration, the structure of the ground portion are complicated.
By revealing the structure and the formation and maintenance factors of biological communities in this environment, to elucidate the maintenance mechanism of woodlands of biodiversity.
The Quercus forest, rather than the main purpose timber production, is necessary for agricultural production and firewood and the farm life such as charcoal or fallen leaves, and it have functions to preserve the farmland and villages as a windbreak forest for arable land and water conservation forest.
The felled quercus makes the charcoal and mushroom logs. The stump becomes forest again by reproduction by spout and the fallen leaves on the surface has been used as compost and germination floor using a heat of fermentation.
The quercus secondary forest has been maintained unique biodiversity by anthropogenic forest management, such as weeding, logging, reproduction by spout and falling leaves collection.
As for the maintenance of the quercus forest of Satoyama, there are height of ability for germ, reproduction and the symbiosis with mycorrhiza bacteria.
The display of multiple functions of quercus forest is expected in the future. It is necessary to clarify the fertility of soil maintenance system.
In addition, the maintenance activity by citizen, civic group and NPO/NGO is indispensable to biological diversity maintenance in the Satoyama area. And, we perform a related policy proposal, support of the activity in the spot continuously.
1) Does act of man act on maintenance mechanism of the biological diversity in the Satoyama?
2) The relationship between the species diversity of land use and plant changes and satoyama plant species composition due to the difference in the wooded area of management
3) Forest floor vegetation has declined by increase of sika deer browsing. Soil erosion and outer layer collapse occur by the decline of the forest floor vegetation at the hillside slope, and measures mechanic to prevent soil erosion and collapse is necessary.
4) Understanding structuring forces and actions for conserving freshwater biodiversity.
Reference articles and patents
1) Toda, H.(2013)3.1. NATURAL ECOSYSTEMS AND SATOYAMA UTILIZATION. (in Research Approaches to Sustainable Biomass Systems, Tojo, S and Hirasawa, T., 399pp., Elsevier). 19-30.
2) 森林立地学会編(2012)森のバランス.東海大学出版会.pp.300.
3) 吉川正人・泉団・星野義延.2013.冬季に火入れ管理される栃木県箒川の河辺草原植生の組成的特徴.植生学会誌,30(1):1-15.
4) 鈴木晴美・吉川正人・星野義延.多摩川扇状地の農業水路における水生植物の分布.2014.植生学会誌,31(2):90-103.
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)