Big data analysis of thermal fluctuation for nanotechnology
Research members: Itsuo Hanasaki PhD.
Research fields: Mechanical engineering
Departments: Organization for Promotion of Tenure-track System, Institute of Engineering
Keywords: Nano/Micro Systems, Fluctuation, Measurement
Web site:
Summary
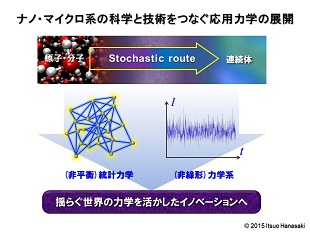
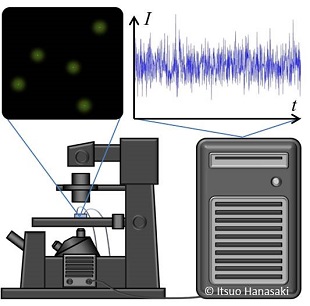
Development of measurement technologies requires the theoretical methodologies. In general, theoretical work plays an essential role when sufficient precision, resolution, and amount of data become available. Now that nanotechnologies are actively focused in the engineering fields and industries, more data are available than before. Microscopic systems show a general feature that the fluctuations of the physical quantities compared to their mean values are significant. Fluctuations are often regarded as just a noise from the macroscopic viewpoints, but fluctuations that originate from the systems of interest themselves often include valuable information as well. In fact, the dynamic light scattering (DLS), which is already widely used in industries, makes use of the time series data of the scattered light fluctuation to evaluate the effective size of particles suspended in fluids. The sufficient amount of data is essential for the significant evaluation of statistical quantities. It is a key concept to make use of the big data of thermal fluctuation for the development of measurement technologies for various phenomena where collective behaviors of atoms, molecules, and other microscopic particles are of great interest. We are developing theoretical methodologies to characterize the systems of interest from the big data of fluctuation based on the statistical mechanics and dynamical systems.
Reference articles and patents
・Itsuo Hanasaki and Yoshitada Isono, "Detection of diffusion anisotropy due to particle asymmetry from single-particle tracking of Brownian motion by the large-deviation principle", Physical Review E, Vol.85, 051134 (9 pages), 2012.
・Itsuo Hanasaki and Satoyuki Kawano, "Evaluation of bacterial motility from non-Gaussianity of finite-sample trajectory by the large deviation principle", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol.25, 465103 (9 pages), 2013.
・Itsuo Hanasaki, Ryo Nagura, and Satoyuki Kawano, "Coarse-grained picture of Brownian motion in water: Role of size and interaction distance range on the nature of randomness", The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol.142, 104301 (11 pages), 2015.
・Itsuo Hanasaki, Satoshi Uehara, and Satoyuki Kawano, "Role of time scales for the non-Gaussianity of the Brownian motion combined with intermittent adsorption", Journal of Computational Science, in press.
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)
